Submarine pipelines in deepwater are mostly laid directly on the seabed. To place a pipeline securely on the seabed, the seabed should be ideally as flat and regular as possible. However, that is not the case many times due to the presence of various geophysical features on the seabed. If such geophysical features make the seabed irregular or undulating, then pipeline may face the risk of spanning and overstressing beyond the allowable limits leading to catastrophic failure. In shallower waters, pipelines may get unstable due to close exposure to waves, currents and tidal movements. Pipelines may require to be installed in a trench or buried in the seafloor to prevent the pipeline from overstressing due to such instabilities. At shore approach location, pipelines shall be buried to protect the pipeline from fishing or third-party intervention as per code requirements.
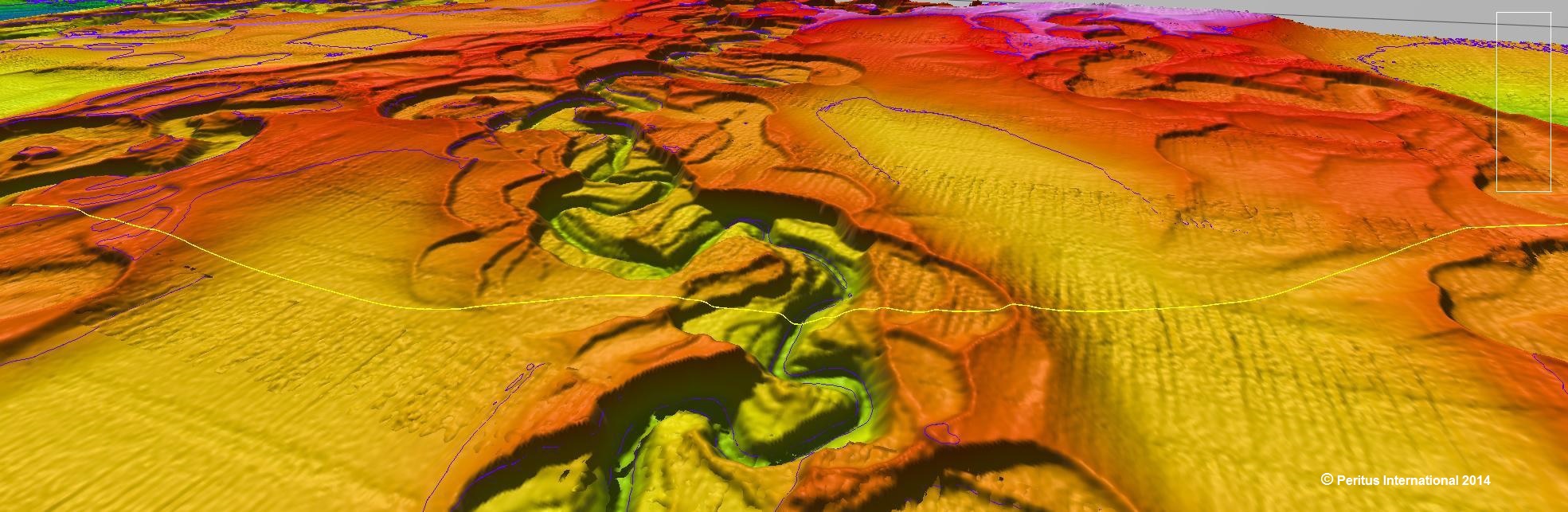
Once the submarine pipeline is laid, scouring of the seabed may take place beneath the pipeline resulting in the creation of long spans. In such situations, the pipeline may require the installation of supports at the free span location to prevent overstressing or fatigue failure of the submarine pipeline due to vortex-induced vibrations (VIV) etc. Also sometimes, the low temperature of the seawater may result in a sharp drop in the temperature of the service fluid resulting in congealing of the service fluid inside the submarine pipelines. Pipelines may be partially insulated from direct contact with the seawater by flush burying the pipeline on the seabed.
All the above situations may call for employment of specialized techniques for the seabed preparation for as-planned installation and safe operation of the pipeline. These techniques are collectively referred to as “
Seabed Intervention”. The process of carrying out seabed intervention is complex, expensive and adversely affects the overall project schedule by stretching the pipeline installation period. Therefore, the pipeline should ideally be routed avoiding all undesirable seabed features. However, this may not always be practically possible and despite the best efforts of the pipeline designer, the requirement of seabed intervention cannot be completely eliminated. Thus, attempts are made during the finalization of pipeline routing to minimise the quantum of seabed intervention works required.